COUNTRY INFORMATION
Official name
Republic of Croatia
Capital
Zagreb
Coordinates
45°10’ N, 15°30’ E
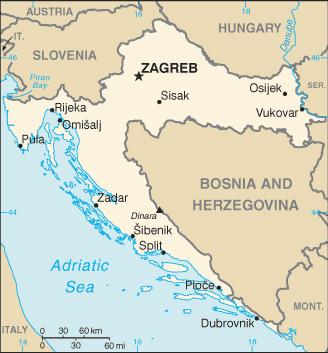
Location
Croatia is located in southeastern Europe and shares borders with Slovenia on the west, Hungary on the north, Serbia and Montenegro on the east, Bosnia and Herzegovina on the south and east, and the Adriatic Sea on the west. Croatia's territory includes 1 185 nearby islands in the Adriatic Sea.
Area
Total area: 56 542 sq km
Land area: 56 414 sq km
Water area: 128 sq km
Land boundaries
2 197 km
Coastline
5 835 km
Administrative division
Croatia is divided into 20 counties (zupanije).
Political system
Croatia is a democratic republic. The Croatian Parliament (Sabor) consists of c. 100-160 members elected every four years. The Croatian Government (Vlada) is composed of fourteen ministers and two deputy prime ministers. The president is elected every five years.
Population
4 491 543
Ethnic groups
Croats 90%, Serbs 4%, other 6%
Religions
Roman Catholic 88%, Orthodox 4%, Muslim 1%, other 7%
HISTORY
Prehistory
Today’s Croatia has been inhabited as early as the beginning of the Stone Age. The Neolithic period belonged to Starčevo, Vučedol and Hvar cultures. The following, the Iron Age, was the period of Hallstatt culture and La Téne, the Celtic culture.
Ancient Times
There are proofs that in the 6th century BC people inhabiting Croatia traded with the ancient Greeks. In the ancient times, the area was colonized by the Illyrians, Celts, Greeks, and finally by the Slavs in the 7th century. Before long the Croats settled in the area.
Middle Ages
Croatia was divided into two dukedoms: the duchy of Pannonian Croatian and the duchy of Littoral Croatia. The Middle Ages brought also Christianization which was completed in the 9th century. A period of constant struggle for supremacy begun. The Croats defended themselves against Bulgarians, Arabs and the Byzantine army and expanded their territory.
Kingdom of Croatia
Kingdom of Croatia begun in 925 when Tomislav was crowned. He and the following rulers again fought against Bulgarians. In the times of King Tomislav, Croatia was one of the most powerful states in Europe. The dynasty ruled until the Battle of Gvozd Mountain in 1097. by virtue of the treaty from 1102, the Croats recognized the Hungarian rule. In this period, many Benedictine monasteries were founded.
Union with Hungary
Croatia shared a new state with Hungary from 1102 to 1526. kings were crowned twice (with the Hungarian and the Croatian crown). New rule introduced feudalism. Noble families became important and tried to regain control. In 1202 Zadar head to bear the aggression of Venetians and Crusaders. In 1409 Dalmatia was sold to Venice. In the end of the union-era, the Croats defended themselves against the Turks and lost some territories. The struggle fro supremacy continued till 1991.
Habsburgs, Venetians and the Ottomans
Hungarian rule over Croatia ended in 1526 when King Louis II died. Croatia was overtaken by the Habsburgs (1527-1918). The Ottomans did not cease to attack Croatia and expanded their territory at the cost of the Croats. In the 18th century, Croatia was ruled by Napoleon and later by the Austrian monarchy. The following period meant Italy and Austria fighting for supremacy over Croatia. Finally, in the battle of Vis in 1866, Italy was defeated. Two years later, Croatian autonomy was restored (Hungarian-Croatian Settlement).
World Wars
From 1918 to 1929 Croatia was a part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenians. In 1929 the Kingdom was renamed Yugoslavia and endured till 1941. Since 1945 to 1991 Yugoslavia was a a communist state. During the two World Wars, Croatia remained an important area of battle. After World War II, a rebuilding process and industrialization started. Despite the country’s socialist system, Croats could travel and have better conditions that countries in the Eastern Bloc of that time.
However, the constitution declared in 1963 again put the Croats in the position of minority. In 1970-71 Croats rebelled and they organized demonstrations for civil liberties and autonomy, Croatian Spring. The protest was suppressed and the leaders were imprisoned. In 1974 a new constitution was declared. First free elections were held in 1990. On 25 June 1991 Croatia declared independence. However, it took some time to completely. separate from Yugoslavia.
Republic of Croatia
Croatia became a member of the Council of Europe in 1996. Since 2000 the country is a member of World Trade Organization. In 2003 Croatia applied for European Union membership.

